Do you ever think about what a verb is and how many kinds there are? Verbs are super important in language because they show actions or tell us about something. In this article, we’ll talk about what verbs are and the different types in both Urdu and English. We’ll use examples to make it easy to understand.
Definition of Verb:
A word that shows something happening, being, or doing is called a verb.
Examples:
Here are some examples of verbs:
- Read
- Write
- Come
- Go
- Play
- Is
- Am
- Are
- Have
- Has
- Had
- And many more!
Sentences:
Abdullah is a player.
The boys are singing a song.
We have a beautiful car.
Types of Verbs
- Transitive verb
- Intransitive verb
- Dynamic verb
- Stative verb
- Auxiliary verb
- Linking verb
- Emotive verb
- Factual verb
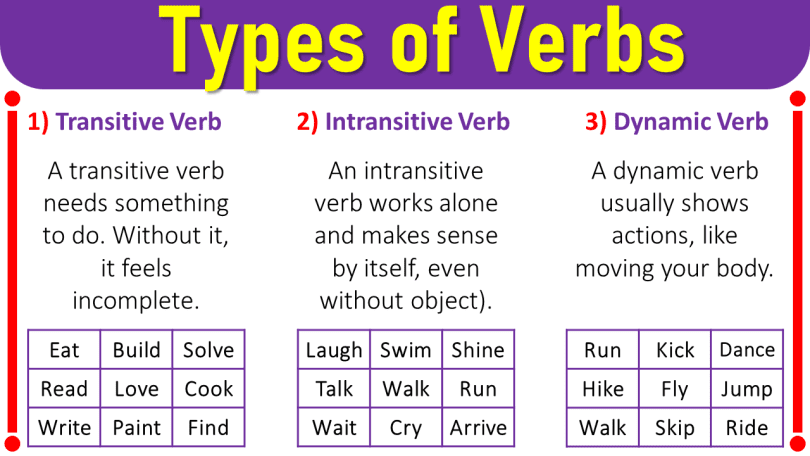
- Transitive Verb:
A transitive verb needs an object to have a clear and complete meaning. Without an object, it’s like it’s missing something.
List of Transitive Verbs:
| Eat | Read | Write | Build |
| Love | Paint | Solve | Cook |
| Find | Watch | Kick | Open |
| Play | Clean | Repair | Sing |
| Drive | Complete | Send | Carry |
Examples:
She is eating an apple.
He is drinking water.
She ate the delicious cake.
He read the book last night.
I love my pet dog.
- Intransitive Verbs:
An intransitive verb doesn’t require an object; it provides a clear and complete meaning even without one.
List of Intransitive Verbs:
| Laugh | Shine | Appear | Talk |
| Run | Cry | Wait | Sneeze |
| Arrive | Swim | Walk | Hesitate |
| Sleep | Jump | Sit | Think |
| Sing | Exist | Stand | Listen |
Examples:
The sun is shining.
She is dying.
She laughed loudly.
He ran quickly.
They arrived early.
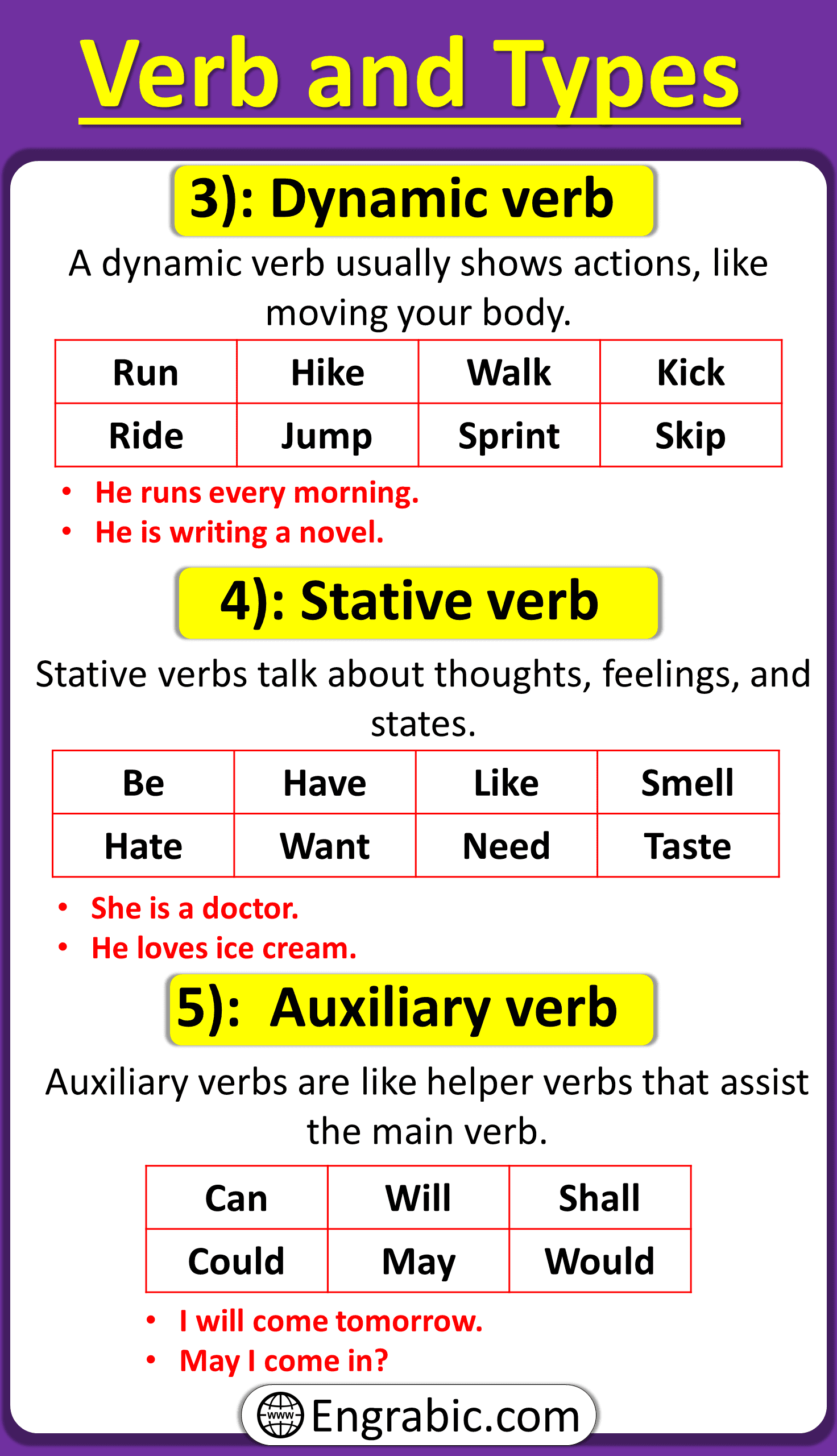
- Dynamic Verbs:
A dynamic verb is a verb that typically involves physical action, events, or movements of hands and legs.
List of Dynamic Verbs:
| Run | Ride | Fly | Hike |
| Jump | Climb | Walk | Sprint |
| Dance | Kick | Skip | Cycle |
| Swim | Punch | Skate | Wrestle |
| Play | Drive | Row | Tackle |
Examples:
He is writing a letter.
She will come tomorrow.
He runs every morning.
I love to swim in the ocean.
He is writing a novel.
- Stative Verbs:
Stative verbs typically express mental feelings, emotions, or the state of a person or thing. They usually involve thoughts and emotions rather than physical actions or movements of the hands and legs.
List of Stative Verbs:
| Be | Hate | Understand | See |
| Have | Want | Remember | Hear |
| Like | Need | Forget | Smell |
| Dislike | Believe | Prefer | Taste |
| Love | Know | Despise | Think |
Examples:
She is a doctor.
They are tired after the long trip.
He loves ice cream.
She hates spiders.
She has a beautiful car.
- Auxiliary Verbs:
Auxiliary verbs, or helping verbs, are like sidekick verbs that help the main verb in a sentence. They give extra details about when, how, or in what way the action happens.
List of Auxiliary Verbs:
| Be(am, is, are, was, were) | Can | Might | Will |
| Have(has, have, had) | Could | Shall | Would |
| Do(does, did) | May | Should | Must |
Examples:
Do you like ice cream?
Is she coming to the party?
I don’t want any more candy.
She is reading a book.
He has finished his meal.
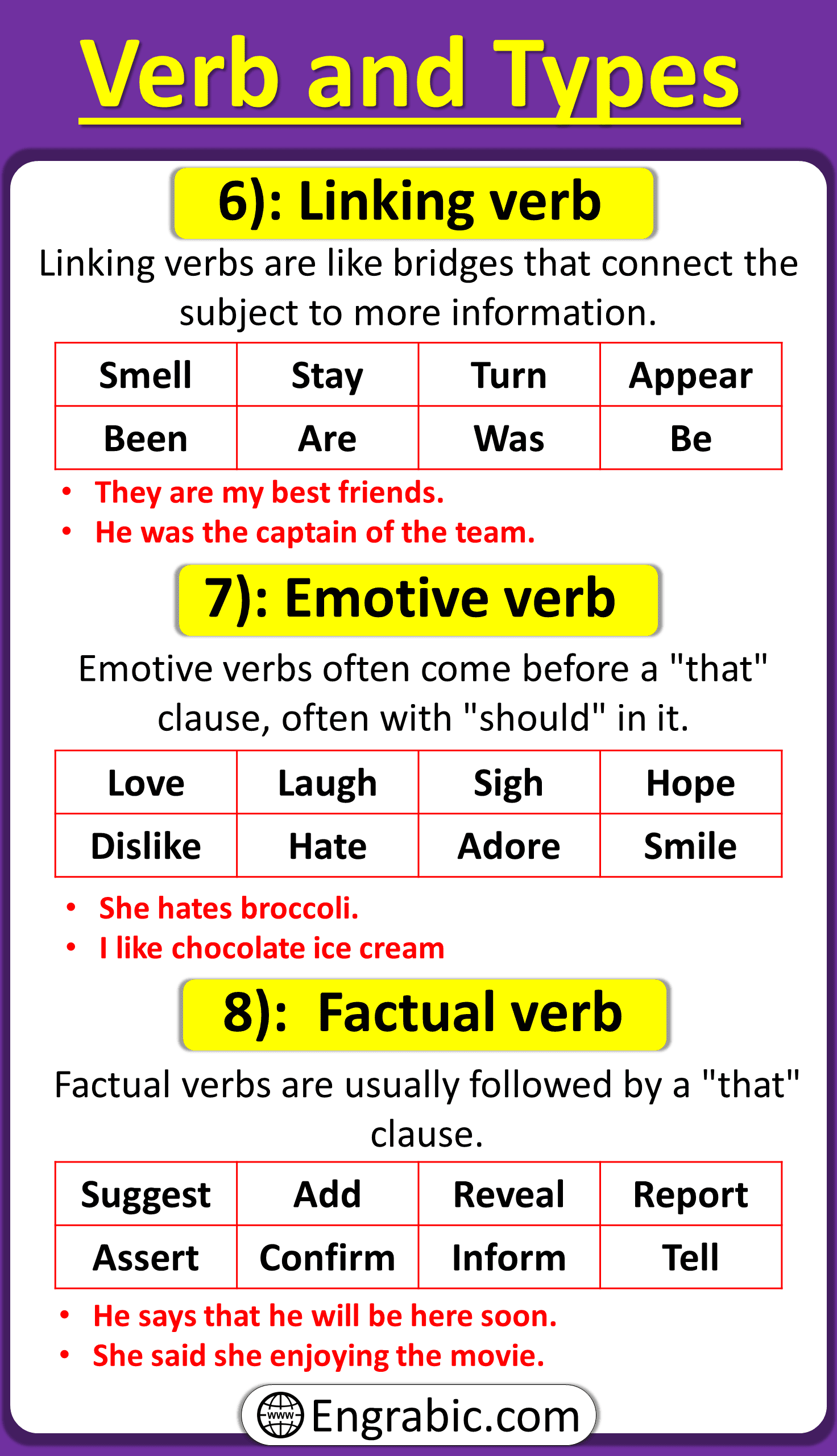
- Linking Verbs:
Linking verbs are like bridges in sentences. They connect the subject and another word to tell us more about the subject. These special verbs, like forms of “be” or “seem,” link the subject to another word in the sentence, which gives us more information.
List of Linking Verbs:
| Am | Be | Appear | Smell |
| Is | Been | Feel | Stay |
| Are | Being | Sound | Turn |
| Was | Seem | Look | Grow |
| Were | Become | Taste | Remain |
Examples:
Uzair is happy.
They are my best friends.
I am a student.
He was the captain of the team.
The flowers were beautiful.
- Emotive Verbs:
Emotive verbs are often followed by a “that” clause, usually with the word “should” in it.
List of Emotive Verbs:
| Love | Dislike | Regret | Laugh |
| Hate | Enjoy | Mourn | Sigh |
| Adore | Fear | Hope | Smile |
| Despise | Appreciate | Wish | Frown |
| Like | Resent | Cry | Pout |
Examples:
She hates broccoli.
He hates when it rains on her birthday.
He despises liars.
She despises waking up early.
I like chocolate ice cream.
- Factual Verbs:
Factual verbs are usually followed by a “that” clause.
List of Factual Verbs:
| Claim | Suggest | Assert | State |
| Announce | Add | Confirm | Explain |
| Mention | Reveal | Clarify | Report |
| Affirm | Inform | Point out | Tell |
| Declare | Acknowledge | Discuss | Say |
Examples:
He says that he will be here by noon.
She said she enjoyed the movie.
He told me that it’s going to rain today.
She explained how the new system works.
She stated her opinion on the matter.
Conclusion:
Verbs are like language superheroes because they let us talk about doing stuff and how stuff is. In both Urdu and English, there are five kinds of verbs: action verbs (for doing things), stative verbs (for saying how things are), helper verbs (they’re like sidekicks), modal verbs (for showing possibilities), and tricky phrasal verbs (a bit confusing). Knowing about these verbs and using them correctly makes us better at talking.



Leave a Comment